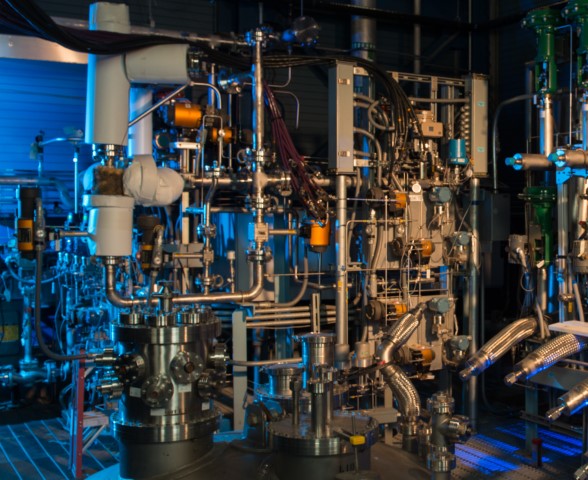
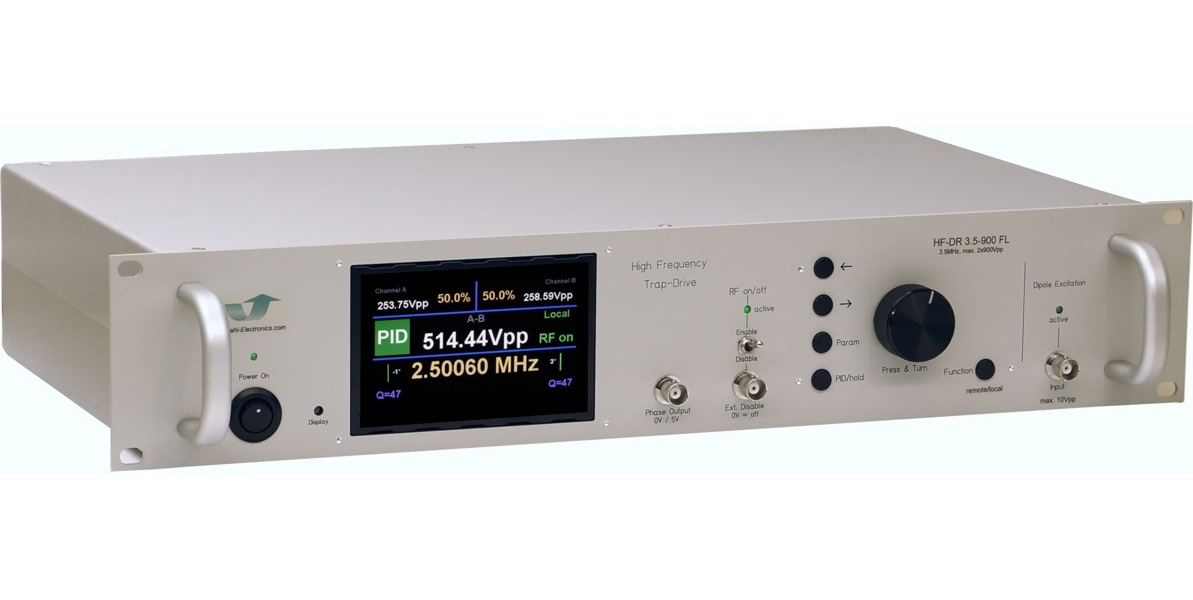
Cryogenic engineering typically requires much customisation for specific experimental setups. Even so, our direct involvement in various scientific projects helped shaping the ambitious device specifications that are critical to success in the common scenarios in industrial as well as scientific environments.
Some recent applications of our cryogenic pre-amplifiers have been:
- multichannel qubit biasing
➜ see our current participation in the qBriqs-Project 2022-2024 - nanoscale surface physics with
shot noise measurements on atomic-size junctions - dark matter research using an
antiproton superconducting tuned detection circuit in a cryogenic Penning trap - beam line monitoring for
single-pass non-destructive electronic detection of charged particles - cryogenic sensors
- scanning tunneling microscopy (STM) / atomic force microscopy (AFM)
- cryogenic transport phenomena
- THz detectors
- quantum point contact (QPC)
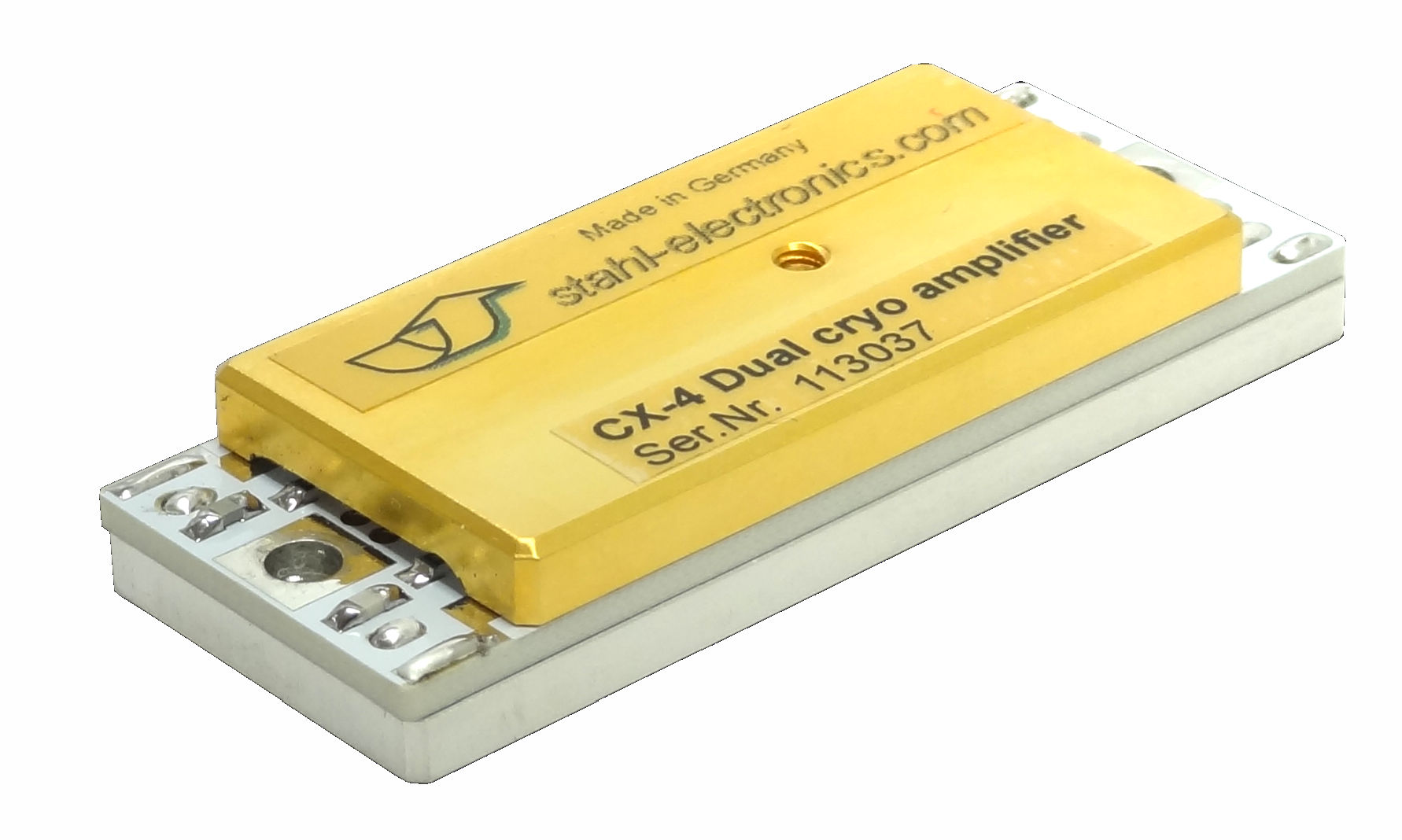
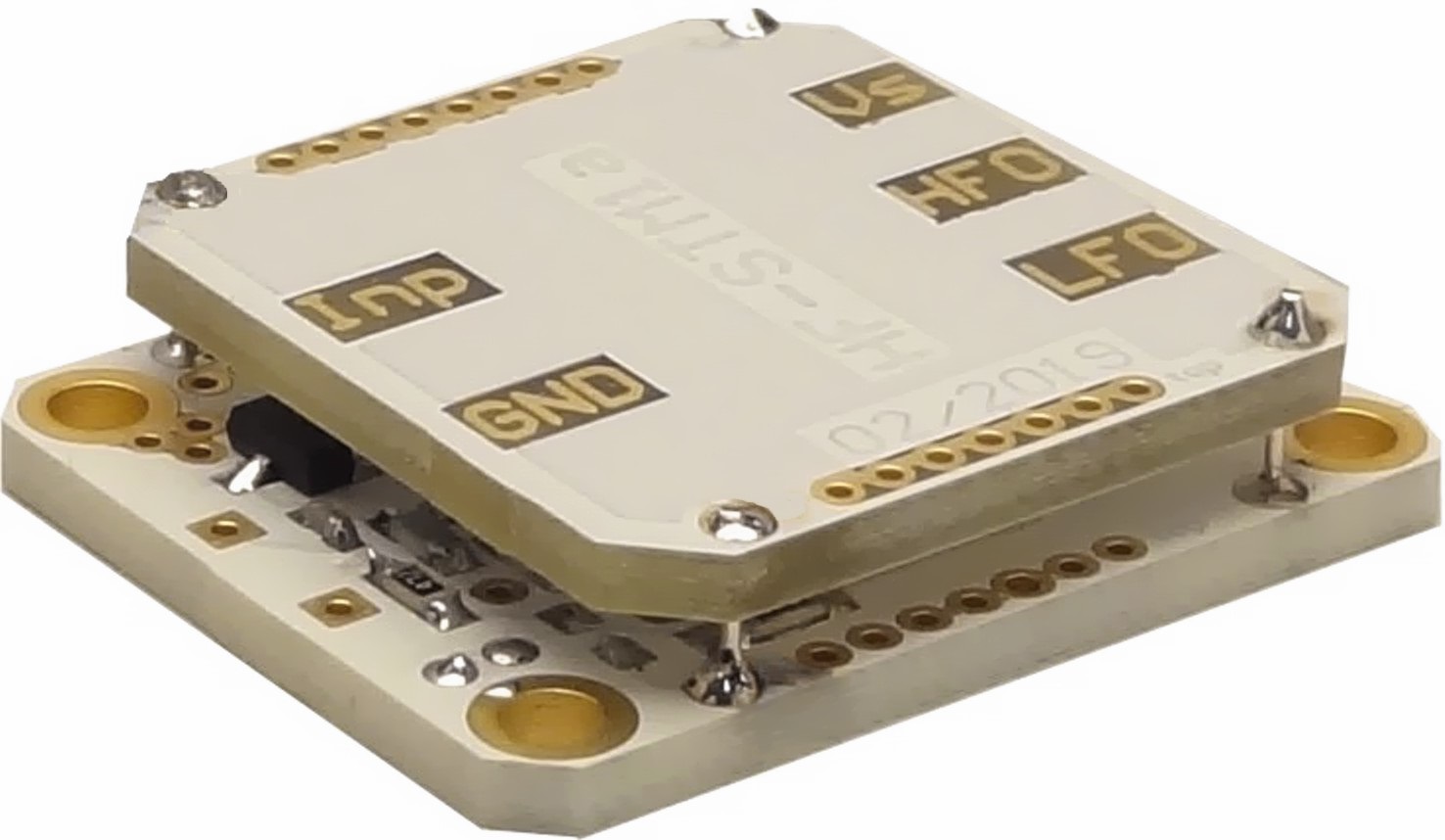
Several standard amplifier systems have been derived from such specific customer projects and are now available for others. These comprise e.g. the CX-4 ultra-low-noise amplifiers, the affordable BUF-series for applications demanding lesser stringent noise performance, and the HF-STM broadband amplifiers, reaching higher frequencies.
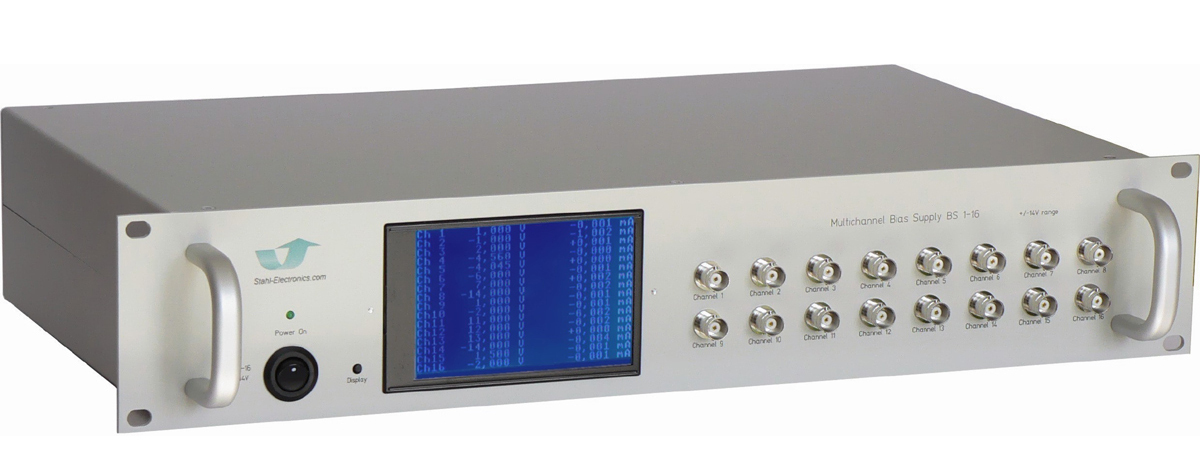
Cryogenic Experiments also benefit from our low-noise bias-sources (BS-series) which have especially been designed to provide highly stable voltages for cryogenic environments.
In the context of funded projects, cryogenic equipment like amplifiers, coupling stages, filters, etc. are being tailored to specific needs - especially, when there is room for future applications.
Depending on the target application, either GaAs components or highly doped Silicon chips may be used. Our GaAs components are manufactured by a specialised foundry and are adapted to cryogenic environments, whereas the Silicon components are produced in standard manufacturing processes.
All our devices are being tested before shipping either in our in-house cryostat systems reaching down to about 3K, or externally in cryostats down to about 100mK.